Loculated Pleural Effusion Ct Scan | There is smooth thickening of the parietal pleura (arrowhead), suggestive (b) nonenhanced ct scan shows a large loculated right pleural effusion displacing the heart contralaterally. Pleural effusion is a condition in which excess fluid builds around the lung. A pleural effusion is accumulation of excessive fluid in the pleural space, the potential space that surrounds each lung. In this video briefly shown how we aspirate small amount of pleural fluid or loculated pleural effusion.for more videos please subscribe the channel.if you. Ct scans show more detail than.
Learn the symptoms and causes, and how it is diagnosed and treated. In this case, at the back because the patient is supine. Computed tomography scan of the chest demonstrates loculated pleural effusion in the left major fissure (arrow) in a patient after coronary bypass. Pleural effusion is an accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity between the lining of the lungs and the thoracic cavity (i.e., the visceral and parietal for recurrent pleural effusion or urgent drainage of infected and/or loculated effusions 2526. (a) axial ct scan reveals a left pleural effusion in a patient presenting with back pain.
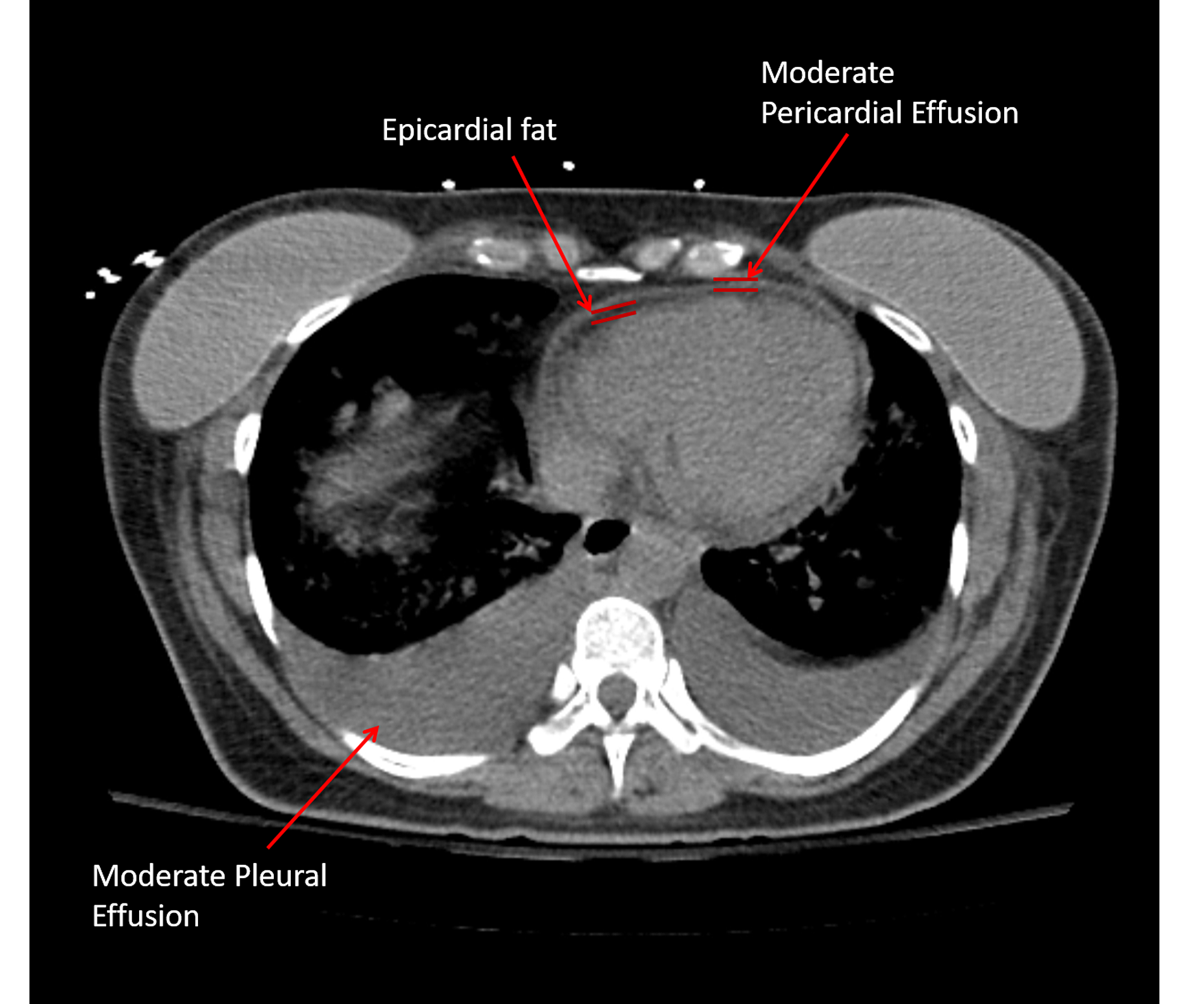
In this case, at the back because the patient is supine. Encapsulation) is most common when the underlying effusion is due to hemothorax conventional chest radiographs and computed tomographic (ct) scans of 70 inflammatory thoracic lesions in 63 patients were reviewed and scored. Note the smooth costal pleural. During this procedure, a needle is used to collect a sample of the fluid in the pleural cavity so it can be looked at under a microscope. Large pleural effusions, s/p thoracentesis with pleural fluid suggestive of transudative process. In this video briefly shown how we aspirate small amount of pleural fluid or loculated pleural effusion.for more videos please subscribe the channel.if you. Conventional chest radiography and computed tomography (ct) scanning are the primary imaging modalities that are used for evaluation of all types of pleural disease, but ultrasound and magnetic resonance. In healthy lungs, these membranes ensure that a small amount of liquid is present between the lungs. Pleural thickening on a ct scan was found to be associated with failure of ipft. A ct scan may be able to diagnose small effusions. Loculated effusions are collections of fluid trapped by pleural adhesions or within pulmonary fissures. Expert gtv segmentations already provided by the nsclc radiomics collection helped inform our segmentations, and areas of the effusion that overlap with gtvs are not included. The fluid usually settles at the lowest space due to gravity;
Loculated effusions are collections of fluid trapped by pleural adhesions or within pulmonary fissures. Loculated effusion) or underlying atelectasis. Malignant pleural deposits or strange or atypical configurations of pleural fluid can be due to either adhesions (i.e. Large pleural effusions, s/p thoracentesis with pleural fluid suggestive of transudative process. Pleural thickening on a ct scan was found to be associated with failure of ipft.
Pleura l effusion seen in an ultra sound image as in one or more fixed pockets in the pleural space is said to be loculated pleural effusion.in us scan us scan they can be identified clearly and it is very complicated.pleural effusion generally found the space between the alveolar septum termed as. Positron emission tomography (pet) scan can help rule out extrathoracic disease that would preclude surgical. Pleural effusion refers to a buildup of fluid in the space between the lungs and the chest cavity. The fluid usually settles at the lowest space due to gravity; Pleural effusion is a condition in which excess fluid builds around the lung. Improved after thoracentesis and diuresis. Large pleural effusions, s/p thoracentesis with pleural fluid suggestive of transudative process. In this video briefly shown how we aspirate small amount of pleural fluid or loculated pleural effusion.for more videos please subscribe the channel.if you. (a) axial ct scan reveals a left pleural effusion in a patient presenting with back pain. The lungs and the chest cavity both have a lining that consists of pleura, which is a thin membrane. Ct scan of the chest of a patient with large loculated pleural effusion in his left thoracic cavity. Pleural effusion segmentations were manually delineated by a medical student and revised by a radiologist. Note the smooth costal pleural.
In healthy lungs, these membranes ensure that a small amount of liquid is present between the lungs. A ct scan may be able to diagnose small effusions. Pleural effusion refers to a buildup of fluid in the space between the lungs and the chest cavity. Ct scanning is excellent at detecting small amounts of fluid and is also often able to identify the underlying intrathoracic causes (e.g. Pleural thickening on a ct scan was found to be associated with failure of ipft.
Positron emission tomography (pet) scan can help rule out extrathoracic disease that would preclude surgical. Ct scans show more detail than. Pleural infection pleural inflammation pleural malignancy pleural fluid analysis findings: Loculated effusions are collections of fluid trapped by pleural adhesions or within pulmonary fissures. Pleural effusion is an accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity between the lining of the lungs and the thoracic cavity (i.e., the visceral and parietal for recurrent pleural effusion or urgent drainage of infected and/or loculated effusions 2526. Note the smooth costal pleural. Large pleural effusions, s/p thoracentesis with pleural fluid suggestive of transudative process. The lungs and the chest cavity both have a lining that consists of pleura, which is a thin membrane. • usually spares mediastinal pleura. Ct scanning is excellent at detecting small amounts of fluid and is also often able to identify the underlying intrathoracic causes (e.g. Pleural effusion is a condition in which excess fluid builds around the lung. A ct scan showing nodular, circumfrential pleural thickening and calcified pleural plaques in a patient who was subsequently diagnosed with mesothelioma. Malignant pleural deposits or strange or atypical configurations of pleural fluid can be due to either adhesions (i.e.
Velg blant mange lignende scener loculated pleural effusion. Ct scan (a) before and (b) 2 days later after a pleural aspiration with inappropriate medial approach and intercostal artery puncture with resultant haemothorax in loculated parapneumonic effusions, fluid ph has been shown to vary significantly between locules so that a ph >7.2 in a patient with other.
Loculated Pleural Effusion Ct Scan: Pleura l effusion seen in an ultra sound image as in one or more fixed pockets in the pleural space is said to be loculated pleural effusion.in us scan us scan they can be identified clearly and it is very complicated.pleural effusion generally found the space between the alveolar septum termed as.
Refference: Loculated Pleural Effusion Ct Scan
Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar